- SE
-
- Abbreviation for special edition.
- An API designation for gasoline engines in passenger cars and some trucks beginning with 1972 and certain 1971 through 1979 models. Oils designed for this service provide more protection against oil oxidation, high temperature deposits, rust, and corrosion in gasoline engines than oils of SD classification which it replaced. It was replaced, in turn, by SF oil. These vehicles can benefit from the modern SM oils.
- Seabee
- A self-propelled sea barge larger than the Lash but using rollers to move aboard the ship

- Sea can
- A completely enclosed, often water tight container designed to be loaded onto ocean freighters to carry commodities overseas. Also called an ocean container.
- Sea chest
- An opening for supplying seawater to condensers, pumps, etc. located in the hull below the waterline and having means for the attachment of the associated piping
- Seal
-
- A flexible ring, disc, or washer that prevents the passage of liquid, air, gas, or dirt.
- To prevent the passage of liquid, air, gas, etc. by means of a seal or sealant (e.g., on seams, joints, flanges).
- To coat a surface (e.g., when undersealing a car) by closing the pores of the anodic oxide layer in order to increase the resistance to staining and its effectiveness against corrosion
See- Apex seal
- Bellows Seal
- Chip Seal
- Crankshaft Seal
- Cup seal
- Door seal
- Dynamic seal
- Flange seal
- Glass seal
- Grease seal
- Mechanical face seal
- Mechanical seal
- Oil seal
- Piston seal
- Primary seal
- Radial shaft seal
- Rotating seal ring
- Secondary seal
- Shaft seal
- Sillment seal
- Slurry seal
- Static seal
- Stem seal
- Stroking Seal
- Sylphon Seal
- Valve oil seal
- Valve stem seal
- Wheel Bearing Seals
- Seal coat
- A process of spraying liquid asphalt on the road surface followed by a layer of crushed rock. A seal coat protects the existing road against water damage, adds traction to the road surface and prolongs its life.
- Sealed beam headlight
- A headlight Lamp in which the lens, reflector, and Filament are fused together to form a single unit. They are relatively inexpensive, but when one component breaks, the whole unit is replaced. Newer vehicles use the more expensive Composite type with separate Bulb and lens which can be replaced individually in the event of failure. Only a few types of Bulbs are used in the Composite headlight, but the lens differs because it is shaped to the contour of the vehicle.
- Sealed beam unit
- A headlight that usually contains twin high/low filaments, a reflector, and a lens and is sealed to keep out dirt and moisture. When the headlight fails, you replace the entire unit. Sealed beam units are usually found on older vehicles. Newer ones have halogen headlights.
- Sealed bearing
- A bearing that has been lubricated at the factory and then sealed, it cannot be lubricated during service. It is sealed to keep out contaminants.
- Sealed bottom bracket
- A bottom bracket with protective seals to keep water and grime from penetrating to the bearings. Also called cartridge bottom bracket
- Sealed unit
- Motor compressor assembly in which motor and compressor operate inside sealed housing. See
- Sealer
-
- A substance you can add to the liquid in the cooling system to seal leaks. Also called stop leak.
- Other kinds of sealing Compounds are used to Coat surfaces before installing hoses or Gaskets. These are effective in preventing leakage but usually make the hose or gasket hard to remove.
- An intercoat between the top Coat and the Primer or old Finish, giving better Adhesion.
- Any material used to fill cracks and pinholes in a metal surface to be painted, applied before the base coat or as a base coat primer-sealer.
- Sealing smut
- Impurity deposit which forms after the anodized aluminum pieces are immersed in hot water
- Sealing strip
- Gas seal to the epitrochoidal surface in a rotary engine, with the same function as the piston ring on a conventional piston engine
- Seamed tubing
- Tubing made from steel strip stock that is curved until its edges meet, then welded together. Contrast Seamless tubing.
- Seamless tubing
- Tubing made from solid blocks of steel that are pierced and drawn into tube shape. Contrast Seamed tubing.
- Seam sealing
- The sealing of seams, usually using organic compounds, to prevent the penetration of corrosive agents. See
- Seat
-
- A surface upon which another part rests or settles. Example: the valve seat is the matched surface upon which Valve face rests.
- Minor wearing of the piston ring surface during initial use. Rings then fit or seat properly against the cylinder wall.
- The cushions on which the driver and passengers rest.
- A metering control that is regulated by a Needle.
See- Baby seat
- Bead seat
- Bench seat
- Bucket seat
- Child Bike Seat
- Child seat
- Conical seat
- Contre pente on both bead seats
- Flat seat
- Folding rear seats
- Front seat
- Front seats
- Inertia reel seat belt
- Infant safety seat
- Innerspring seat
- Integral molded seat
- Integrated child seat
- Integrated child safety seat
- Needle and seat
- Power seat
- Radius seat
- Rear seat belt
- Rim bead seat
- Rim bead seat taper
- R/seat
- rumble seat
- Saddle
- Safety bead seat
- Solo seat
- Split bench seat
- Split folding rear seats
- Split rear seats
- Spring seat
- Taper seat
- Tube Seat
- valve seat
- Valve spring seat
- Seat adjuster
- A device which operates manually or electronically to move the position of the seat cushion forward or backward. It may tilt the front or back of the seat cushion up or down and may also move the seat back forward or back -- even to a reclining position. In some cases the adjuster will allow complete removal of the seat assembly.
- Seat belt
- A passive Restraint system which encircles the hips to prevent the occupant from being ejected from the vehicle. Often the seat belt is part of the shoulder harness. The use of seat belts is mandatory in every province and state in North America and in most every country.
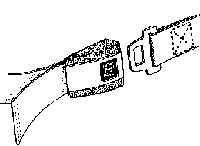
Seat belt
- Seat belt tensioner
- A device that pulls the seatbelt tight in the event of a collision, taking up extra slack and reducing the force with which the occupant's body hits the belt. It is sometimes referred to as a pretensioner, though this implies that it deploys when a crash is imminent, which is misleading. Tensioners are generally tied into the same sensors that trigger the airbags and deploy at the moment of collision.
- Seat belt warning light
- A light on the instrument panel which illuminates or flashes if the seat belts are not fastened.
- Seat cluster
- On a bicycle, the conjunction of Top tube, Seat tube, and Seatstays near the top of the seat.
- Seat cover clip
- A spring steel clip used to secure the front seat sideshield and front seat back panel.

Seat cover clip
- Seat covers
- Trucker slang for attractive women in vehicles as in 'Look at the seatcovers in that westbound rollerskate.'
- Seating buck
- A temporary adjustable seat in a vehicle used in the design stage to determine the best shape and location.
- Seat-integrated belt system
- A seat belt with all belt elements and deflection points integrated in the seat; this improves occupant restraint in every seating position, but particularly sturdy seats and floorpans are required
- Seatpost
- On a bicycle, the part to which the Saddle clamps and which runs down inside the Seat tube.
- Seatpost binder bolt
- A bolt or quick release at the top of the seat tube used to hold the seatpost in place.
- Seat rail console
- A mounting panel for the seat rails, spot-welded to the floorpan; the front consoles are usually somewhat higher than the rear ones to produce the desired angle of the seating surface
- Sea trials
- A series of test runs done at sea to determine whether the ship has met the specifications of design, modification, or repair
- Seatstay
- On a bicycle, one of the two parallel tubes that run from the top of the Seat tube back to the rear dropout.
- Seatstays
- On a bicycle, the two parallel tubes that run from the top of the Seat tube back to the rear dropouts.
- Seat tube
- On a bicycle, the tube that runs from just below the Saddle down to the bottom bracket.
- Seat well
- A sheet metal panel to cover up the area below the car seats, especially below the rear seat bench
- Sea worthiness
- The condition of a vessel with regard to materials, construction, equipment, crew, and outfit which is considered safe for the trade in which it is employed
- Seaworthiness certificate
- A certificate issued by a classification society surveyor allowing a vessel with a mishap affecting its seaworthiness to proceed to another port where permanent repairs can be carried out.
- Secondary
- The high voltage side of the ignition system, usually above 20,000 volts. The secondary includes the ignition coil, coil wire, distributor cap and rotor, spark plug wires, and spark plug
- Secondary air
-
- In some exhaust emission control systems, e.g., thermal reactor or two-bed converter, secondary (outside) air is added to the exhaust to ensure sufficient supply of oxygen to promote oxidation of HC and CO, thus converting these pollutants into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide.
- Air externally supplied to the flame at the point of combustion.
- Secondary air anti-backfire valve
- A check valve that prevents exhaust system backfires from entering the secondary air system.
- Secondary air bypass valve
- An electronically controlled solenoid/vacuum valve that directs secondary air from the air pump to the atmosphere or to the secondary air switching valve.
- Secondary air pulse valve
- A valve activated by exhaust that uses the negative pressure pulses in the exhaust to draw secondary air into the exhaust system.
- Secondary air switching valve
- An electronically controlled solenoid/vacuum valve that directs secondary air from the pump to either the catalytic converter or the exhaust ports of the engine.
- Secondary braking system
- (HGV) A spring brake system which exerts force when air pressure is released
- Secondary circuit
-
- The high voltage part of the ignition system.
- The circuit which comprises the secondary winding of the ignition coil, the distributor, and the spark plugs
- Secondary compression
- A term that is used in two-stroke engines. Primary compression takes place in the crankcase and is then pushed up into the combustion chamber where secondary compression takes place as the piston squeezes the mixture. If the crankcase seals are poor, Primary compression will be reduced resulting in reduced secondary compression so that it may be difficult to start the engine.
- Secondary controls
- Devices in a vehicle that do not direct its movement or braking but control how the driver sees out of the vehicle and how the vehicle is seen; examples are de-misters, windscreen wipers, washers and hazard lights
- Secondary failure
- The failure which occurs as a result of a primary failure (e.g., the primary failure is a flat tire caused by a nail hole; but as the tire continues to run flat, the secondary failure may be a tire roll-off where the tire comes off the rim). A good mechanic will search for the primary failure so that a secondary failure will not be repeated.
- Secondary ignition
- The high-voltage part of the ignition circuit, such as part of the ignition coil wiring, spark plugs, spark plug wires, distributor cap, and rotor. Compare Primary ignition
- Secondary key
- A key which operates only the locks needed for valet parking, i.e., door locks, ignition switch, and steering column lock; does not allow access to trunk, glove box, etc.
- Secondary operations
-
- Less important than the major steps of heading or cold forming fasteners, secondary operations include grinding, polishing, drilling.
- Operations which include punching, shaving, trimming, drilling, sawing, milling, pointing, tapping and polishing, etc., are generally called secondary.
- Secondary piston
-
- In a dual or tandem master cylinder, it is the piston which is normally pushed forward by fluid trapped between it and the primary piston.
- In a tandem master cylinder, a floating piston which isolates the two braking circuits from each other and actuates the secondary circuit
- Secondary pump
- An oil pump driven via the gearbox output shaft. Compare Primary pump
- Secondary refrigerating system
- Refrigerating system in which the condenser is cooled by a different evaporator from the primary refrigerating system.
- Secondary seal
- A secondary piston seal in a tandem master cylinder
- Secondary shoe
-
- The shoe in a duo-servo drum brake assembly that is acted upon by the primary shoe. It provides more stopping power than the primary shoe (about 70%).
- The rear shoe in a drum brake; often has longer lining than the other shoe.
See
- Secondary visor
- In a dual visor system, the main visor is moved to the side and the secondary visor is flipped down, thus shielding the driver from the sun from both the front and side
- Secondary winding
-
- An inner winding of the ignition coil; typically 20,000 to 30,000 turns of very fine wire. The opposite is primary winding
- The secondary winding of an electric motor is a winding that is not connected to the power source but carries current induced in it through its magnetic linkage with the primary winding
- Secondary wires
- The high voltage wire from the Coil to the distributor tower and from the tower to the spark plugs.
- Second gear
- A middle gear which has a faster ratio than low gear, but slower than high gear. It is used for climbing or descending steep hills
- Second law of thermodynamics
- Heat will flow only from material at higher temperature to material at lower temperature.
- Section height
- The vertical measurement from the bead seat of a tire to the top of the crown when it is mounted, inflated and not under load. (Overall diameter less nominal rim diameter, divided by two.)
- Section repair
-
- Reinforcement made to the Casing when an injury has extended through the tread or sidewall of a tire. The damaged cord is removed and a new cord is replaced in the form of a repair unit or patch.
- A major repair in the sidewall or tread of a tire. This repair unit must have cord material for reinforcement, made specifically for the type of tire -- bias-ply or radial.
- An effective and economical repair method where extensive damage is confined to a specific section of the body shell and an undamaged section is taken from a vehicle which has been written off
- Section width
- The measurement across the tire width at the widest point when mounted and inflated (not under load), excluding any decorative moldings.
- Sedan
- The term sedan originally described a conveyance seen only in movies today -- a wheelless vehicle for one person, carried on poles by two men, one ahead and one behind. Automakers borrowed the word and applied it to cars with an enclosed four-door body type, permanent back panels, and top with full-width cross seats front and rear, and passenger capacity from five to seven depending on wheelbase. Longer-wheelbase models accept extra passengers in fold-down auxiliary seats. Sedans usually have quarter windows in the rear quarter in addition to windows in all four doors. trunk racks often were standard offerings. Called saloon in U.K. According to Car and Driver, the term 'sedan' refers to a fixed-roof car with at least four doors or any fixed-roof two-door car with at least 33 cubic feet (934 litres) of rear interior volume, according to measurements based on SAE standard J1100.

Sedan
- Sedanca
- An early body style in which the top extended for a quarter of a circle and covered only the passengers in the rear seats.
- Sedanette
- A two-door sedan having a slanted back with the rear window and trunk along one unbroken curve. This name for the early streamlined design is most often used for Buick and Cadillac models, but similar designs of other makes are known by various names such as 'Aero' (Chevrolet), 'Jetback,' 'Streamliner' (Pontiac), 'Torpedo,' and simply 'fastback.'.
- Sedanet
- A two-door sedan having a slanted back with the rear window and trunk along one unbroken curve. This name for the early streamlined design is most often used for Buick and Cadillac models, but similar designs of other makes are known by various names such as 'Aero' (Chevrolet), 'Jetback,' 'Streamliner' (Pontiac), 'Torpedo,' and simply 'fastback.'.
- Seebeck effect
- When two different adjacent metals are heated, an electric current is generated between the metals.
- Seed
- A paint fault where a uniform distribution of small particles of regular size and pattern exist in a paint film. It is caused by contamination of the paint and poor filtration of the air lines. It is not to be confused with dirt contamination which is caused by dust settling on the painted surface before it has dried
- SEER
- Abbreviation for Seasonal energy efficiency ratio.
- SEFI
- Abbreviation for Sequential electronic fuel injection
- Segregated cycle route
- (SCR) A pathway dedicated exclusively for bicycle and not for pedestrians or other vehicles. Unlike Multiple-use paths.
- Seize
-
- The condition when two items bond together so that they cannot be removed easily.
- The condition when a piston bonds itself to the sides of the cylinder wall because of the lack of lubricant or overheating.
See
- Selectable four-wheel drive
- A four-wheeled vehicle which proceeds normally in two-wheel drive but on which, by means of a lever control, four-wheel drive may be selected. It is important to remember that such vehicles in four-wheel drive do not have the benefit of a center differential
- Selective absorber surface
-
- Surface used to increase the temperature of a solar collector.
- A solar absorber surface that has high absorbtance at wavelengths corresponding to that of the solar spectrum and low emittance in the infrared range.
- Selective Catalytic Reduction
- (SCR) Term frequently used as a synonym for catalytic reduction of NOx in diesel exhaust or flue gases by nitrogen containing compounds, such as ammonia or urea. Such SCR systems are commercially available for stationary applications and are being developed for mobile diesel engines. Since selective catalytic reduction is a generic term which also applies to other reactions, its use may lead to confusion in some situations.
- Selective corrosion
- The corrosion of alloys where the components react in proportions differing from their proportions in the alloys
- Selective transmission
- The conventional manual transmission of today in which any gear may be selected at will as opposed to the very early Progressive transmission in which the gears had to be selected in order.
- Select-low principle
-
- The method by which the rear brake application of an ABS brake system is monitored and controlled, based on the rear wheel with the least amount of traction
- The controlling principle for rear-wheel anti-lock systems which states that pressure to both wheels shall be limited to the level required by the wheel with the least traction.
- Selector fork
- A part of the selector mechanism of a manual gearbox, shaped like a two-pronged fork, which fits into the groove round a coupling sleeve and moves a sliding pinion forward or back along a selector rod

Selector Fork
- Selector lever
- An automatic transmission lever which permits the driver to adapt the gearchanging processes to particular road or driving conditions (slippery road surface, hilly terrain, towing) by choosing one of the drive ranges. Reverse, neutral, and parking lock are also selected by means of the selector lever
- Selector lever lock
- A device which locks the selector lever in Neutral or Park unless the driver depresses the brake pedal
- Selector rod
- A rod running the length of the transmission, along which the selector fork travels
- Self-adjusting
- A mechanism that adjusts itself to compensate for wear or to maintain a certain distance or heat level
- Self-adjusting drum brakes
- A brake that automatically maintains the correct clearance between the lining and the drum.
- Self-aligning torque
- A torque which is created by the tire when the vehicle corners. The force created at the tire Patch acts toward the rear of the actual center of the wheel. This action is called pneumatic trail. It has the same effect as positive Caster and can be increased by increasing the positive Caster. Thus the Trail distance (distance from the point at which the cornering force acts to the center of the wheel or Steering axis) is a moment arm that results in a torque that tends to decrease the existing Slip angle and force the wheel back to the straight-ahead position. This self-aligning torque is transmitted through the steering mechanism to the steering wheel and can be felt as steering effort or Road feel.
- Self-cancelling indicator
- All modern signal light switches (direction indicators) switch off automatically when the steering wheel is returned to the straight-ahead position
- Self-centering
- The forces in a steering system that set the front wheels straight when the driver's grip on the steering wheel is released after cornering
- Self-centering effect
- The forces in a steering system that set the front wheels straight when the driver's grip on the steering wheel is released after cornering
- Self-cleaning
- The ability of a spark plug to burn off the deposits of carbon and oil which build up due to tracking across the tip
- Self-cleaning tread
- A tread pattern with tapered grooves and ribs, bars, etc., arranged in a manner that resists packing loose materials, (mud, etc.) in the grooves.
- Self-contained
- Having all essential working parts, except energy and control connections, so contained in a case or framework that they do not depend on equipment or fastenings outside of the machine.
- Self-diagnosis
- A test function in electronic engine management systems with a test program monitoring input and output signals, detecting errors and storing them permanently in a fault memory
- Self-diagnostic code
- The ECM can detect malfunctions in the CCC systems. If a malfunction occurs, the ECM turns on the check engine light. A diagnostic code can be obtained from the ECM through the check engine light. This code will indicate the area of the malfunction
- Self-energizing
- A brake shoe that is forced into the drum by the movement of the drum. A self-energizing shoe is mounted so its friction surface leads or is ahead of its pivot point.
- Self-energizing action
- The action of a rotating brake drum that increases the application pressure of the brake shoe(s).
- Self-energizing brake shoe
- A brake shoe (sometimes both shoes) that when applied develops a wedging action that actually assists or boosts the braking force applied by the wheel cylinder. See
- Self-ignition
- The ignition of the air/fuel mixture in a diesel engine caused by high pressure and temperature. Different from a Spark ignition
- Self-induction
- This occurs when the current in an inductive circuit changes and the magnetic field cuts the conductors; this induced electromotive force opposes the change in current, restricting it if the current is increasing and enhancing it if the current is decreasing
- Self-induction back-voltage
- Back-voltage produced by self-induction. This induced electromotive force opposes the change in current, restricting it if the current is increasing and enhancing it if the current is decreasing.
- Self-leveling strut
- A suspension strut incorporating a shock absorber with a rubber boot filled with compressed air, serving as an auxiliary pneumatic spring
- Self-Locking
- Where binding action is self-induced on the body of the bolt, screw or nut to keep it rigid and prevent movement and vibration.
- Self-parking
- The ability of a car to park automatically, without any input from the driver; introduced by the VW Futura in 1991
- Self-parking wiper
- A windshield wiper that automatically returns to the (horizontal) park position when switched off
- Self-regulating sheathed-type glow plug
- Originally a sheathed-type glow plug with a self-regulating heating coil, now with a heating and regulating coil
- Self-sustaining ship
- A containership fitted with her own crane for loading and discharging containers
- Self test
- A part of functional diagnostic test procedure that verifies operation of sensors and actuators, detects hard faults, and stores information for later retrieval
- Self-vulcanization
- Vulcanization at room temperature or above, activated by chemical agents without the application of heat from an outside source.
- Sem
- A preassembled fastener, consisting of any type of screw or bolt, furnished with a toothed washer See
- SEMA
- Abbreviation for Specialty Equipment Market Association, the aftermarket and Reproduction vehicle parts organization.
- Semaphore indicator
- A signal light indicator used before flashers were introduced (such as on the Austin and Flying Standard), consisting of a lighted arrow that popped out from the side of the car (usually the B-post) when the turn signal switch was actuated. Also called trafficator

Semaphore indicator
- Semi-active suspension
- A suspension whose characteristics can be tuned to driving conditions, such as by hydraulic adjustment of spring supports plus electronic correction of the damping rate
- Semi-automatic frost control
- Control which starts defrosting part of a cycle manually and then returns system to normal operation automatically.
- Semi-automatic transmission
- A transmission in which the clutch is disengaged and re-engaged automatically when the driver actuates the gear lever
- Semiconductor
-
- A solid material such as silicon that has a resistivity midway between that of a conductor and a resistor, with properties of both a conductor and an insulator; used as substrates for semiconductor devices such as diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits
- Any material that has a limited capacity for conducting an electric current. Certain semiconductors, including silicon, gallium arsenide, copper indium diselenide, and cadmium telluride, are uniquely suited to the photovoltaic conversion process.
- Semiconductor ignition system
- An ignition system that uses semiconductors for the switching operations
- Semi-diesel
- A semi-diesel engine operates on comparatively high compression and uses solid injection of fuel, however, it does use an electrical ignition system rather than depend solely upon heat generated by compression to furnish ignition
- Semi-drop center rim
- (SDC) A wheel rim having a demountable flange, for use on light commercial application. A slight depression in the center of the rim facilitates tire mounting and removal.
- Semi-drying oil
- Those oils which are only partially hardened or are changed into a sticky mass when exposed to air and sunlight. The chief semi-drying oils used in paint, varnish, and lacquers are soybean oil, corn oil, and cotton-seed oil.
- Semi-elliptic springs
- A type of Leaf spring that takes its name from the shape which is part of an ellipse.

Semi-elliptic springs
- Semi-Finished Hexagon Bolts
- Bolts with standard sizes ranging from 1/4' through 4'. Class 2A tolerance. The bearing surface is washer faced.
- Semi-floating axle
- Type of axle commonly used in modern vehicles. The outer end of the axle shaft does two things (1) it supports the weight of the vehicle and (2) it is the means of propulsion. The inner end of the axle shaft which is Splined, floats in the Differential gear. In this design a single bearing is placed between the axle shaft and the axle bearing; to remove the axle the wheel must first be removed.
- Semi-independent suspension
- A rear axle design with a torsionally flexible crossmember, the wheels being located on trailing links
- Semi-metallic lining
-
- Brake lining incorporating a high-percentage of metal in its composition.
- A heavy-duty lining molded from iron powder, steel fibers, and organic binders works especially well at high temperatures.
- Semi-race cam
- A type of camshaft for race car engines which increases lift of valve, speed of valve opening and closing, length of time valve is held open, etc. Also called Full cam, Three-quarter cam, or Race cam, depending upon design
- Semislick tire
- A type of mountain bicycle tire with limited tread; popular for not-too-technical courses because it rolls faster than a knobby tire
- Semi-trailer
-
- A type of trailer that has wheels only at the rear, the front is supported by the towing vehicle or a dolly
- The front portion of a semitrailer rests on the back of a tractor. The semitrailer is coupled to the tractor by the fifth wheel on the tractor and the kingpin on the trailer. A semitrailer has no front axle and cannot stand without support. Semitrailers are pulled by tractors only. A trailer whose front half rests on the back of a tractor, coupled to the tractor by a fifth wheel.
See
- Semi-trailing arm
- A type of Independent rear suspension where the pivot axes are usually at about 25 degrees to a line running straight across the car. This arrangement gives rear-wheel Camber somewhere between that of a pure Trailing arm (which has no Camber change relative to the body) and a Swing axle (which has large Camber change).
- Semi-trailing link
- An arm of a coil spring, independent rear suspension system which pivots at an angle to the centerline of the vehicle, thus imparting negative camber with increase in load. Also called Semi-trailing arm
- Sems screw
- A machine screw and free-spinning lock-washer manufactured as one assembly. Steel SEMS are available with the following types of washers: internal tooth, external tooth, split-lock and square-cone. Stainless SEMS are offered with external tooth lock washers.
- Sender
- A sensor unit conveying information about an engine to a gauge, warning light, or other component. See
- Sendzimir process
- A continuous strip galvanizing process, named after its inventor. The strip is wound from a coil while the oil or grease adhering to it is removed by oxidation. It is then annealed, and the oxides are reduced by ammonia, after which it is cooled to 500°C and immersed in a zinc bath, which is kept molten at about 45O°C by the heat from the steel strip. On leaving the bath, the strip is cut and coiled
- Senna, Ayrton
- Ayrton Senna (full name Ayrton Senna Da Silva) of Brazil was, without question, the greatest race car driver in history. He was the embodiment of the professional race car driver. From his first appearance in a Grand Prix event in 1984, the racing world was on notice. The man was on a single-minded mission to win a World Championship title. No driver ever pursued this goal with such determination. Senna won his first title in 1988 and then again, two more times, in 1990 and 1992. He sat on the pole for more than 55% of all races he entered. Ayrton Senna was killed during the opening laps of the 1994 Grand Prix of San Marino at the Circuit dino Ferrari near the town of Imola in Italy. His death was mourned the world over. Both Brazil and Japan took national holidays to mourn his passing. At the time of his death, Ayrton Senna was so significant to Brazil as a hero and source of income, he was responsible for nearly 20% of that country's gross national product. His body lay in state in the National Assembly before being buried with full state rights. At the time of this writing, rather pointless charges of manslaughter have been brought against the team Senna drove for at the time of his death. Frank Williams (the team owner), Adrian Newey (team Chief Designer) and Patrick Head (team Technical Manager) all face charges.
- Sensitive bulb
- Part of sealed fluid device which reacts to temperature. Used to measure tem or to control a mechanism.
- Sensitivity
- The percent of speed change required to produce a corrective movement of the governor or other speed control mechanism of an engine.
- Sensor
-
- An electronic detection device that receives and reacts to a signal, such as a change in voltage, temperature or pressure.
- Material or device which goes through physical change or electronic characteristic change as surrounding conditions change.
- Any device that receives and reacts to a signal, such as of a change in voltage, temperature, or pressure. Sends an input signal to a computer.
See- Air Flow Sensor
- Air Mass Sensor
- Air sensor
- Ambient Sensor
- Barometric pressure sensor
- Bimetallic Sensor
- Bimetal Sensor
- Boost sensor
- Camshaft Sensor
- Coolant temperature sensor
- Crank Sensor
- Crankshaft Sensor
- Crash sensor
- Cylinder Sensor
- Detonation sensor
- EGR Function Sensor
- Engine speed sensor
- Engine temperature sensor
- Ground clearance sensor
- Hall-effect sensor
- Hall sensor
- Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor
- Heated Oxygen Sensor
- HEGO sensor
- Impact sensor
- In-car Sensor
- Intake Air Temperature Sensor
- Knock sensor
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor
- Manifold absolute pressure sensor
- Manifold Air Temperature Sensor
- Manifold Charge Temperature Sensor
- Manifold Pressure Sensor
- Manifold Surface Temperature Sensor
- Manifold Vacuum Sensor
- Oil level sensor
- Oil pressure sensor
- Oil Sensor
- Oxygen sensor
- Oxygen sensor system thermo-switch
- PA Sensor
- Pressure Differential Sensor
- Reference mark sensor
- Speed Sensor
- Steering Pressure Sensor
- Switching Sensors
- TA Sensor
- Throttle position sensor
- TW Sensor
- Vacuum sensor
- Vane Air Temperature Sensor
- Variable Reluctance Sensor
- Vehicle Speed Sensor
- Wheel Slip Sensor
- Wheel speed sensor
- Wheel Spin Sensors
- Sensor flap
- A part of an airflow detection device which serves as a measure for the induced air volume; a potentiometer converts sensor flap movement into changes in electrical voltage, a form in which these signals can be evaluated by the fuel injection control unit
- Sensor plate
-
- A plate in the mixture control unit of a CIS, attached to a lever that operates the control plunger in the fuel distributor; the sensor plate position is governed by the amount of air admitted to the engine via the throttle valve and auxiliary air regulator
- A round plate bolted to the air flow sensor lever which floats in the stream of intake air on the CIS type systems
- Separate-application adhesive
- An adhesive consisting of two parts; one part being applied to one face and the other part to the other face and the two faces brought together to form a joint
- Separate chassis
- The traditional body and frame design before the introduction of unitary construction; the body was lowered onto the chassis and bolted to it
- Separate lubrication
- An engine lubrication principle where the oil is no longer mixed with the fuel, but is fed by a metering pump from a separate oil tank to the engine components to be lubricated
- Separation
-
- The parting of retread rubber from the buffed Casing or the parting or debonding of any adjacent parts of the tire (ply to ply, ply to rubber, etc.), usually due to excessive heat.
- After long storage, liquid ingredients of paints and fillers may separate in the can on top of the material; in most cases, this can be overcome by stirring the contents of the can thoroughly before use.
- Separator, oil
- Device to separate refrigerant oil from refrigerant gas and return the oil to compressor crankcase.
- Separator plate
- A solid piece of electrically conductive material (usually a metal or graphite) that is inserted between cells in a stack.
- Separators
-
- Generally, anything that physically separates one part from another.
- The wood, rubber, or plastic sheets or plates inserted between the positive and negative plates in a battery to prevent contact.
- A filter or trap.
- Sequential electronic fuel injection
- (SEFI) a computer controlled fuel system that distributes fuel through an injector located in each intake port of the engine. Each injector is fired separately and has individual circuits. Also called Sequential fuel injection (SFI)
- Sequential fuel injection
- (SFI) A computer controlled fuel injection system in which bursts of gasoline are sprayed into the intake ports by injectors at timed intervals. Each injector is fired separately and has individual circuits. Also called Timed fuel injection or Sequential electronic fuel injection (SEFI)
- Serial number
- The individual, consecutive numbering of a product during production. It may be a combination of letters and numbers.
- Series
-
- A particular type of an automobile make and model. For instance, in 1952 Cadillac fielded three series a 62 (with a 126 inch wheelbase); a 60 (with a 130 inch wheelbase); and a 75 (with a 147 inch wheelbase).
- The alignment of electrical components.
- A numerical representation of a tire's aspect ratio. A 50-series tire has an aspect ratio of 0.50.
- A method of connecting several parts in a row so that one feeds into the next.
- Series circuit
-
- A circuit with two or more resistance units so wired that the current must pass through one unit before reaching the other. In contrast with Parallel circuit.
- Electrical wiring; electrical path (circuit) in which electricity to operate second lamp or device must pass through first; current flow travels, in turn. through all devices connected together.
- Series connection
- A way of joining photovoltaic cells or batteries by connecting positive leads to negative leads to increase the voltage. Two twelve-volt batteries connected in series results in an output of 24 volts. Contrast Parallel connection where positive is connected to positive and negative to negative resulting in a stronger 12 volts (i.e., more amperage).
- Series custom
- Custom bodies made up in small batches, usually ranging from five to 25. Also called 'semi custom.'
- Series-parallel circuit
- A circuit of three or more resistance units in which a series and a Parallel circuit are combined.
- Series resistance
- Parasitic resistance to current flow in a cell due to mechanisms such as resistance from the bulk of the semiconductor material, metallic contacts, and interconnections.
- Serpentine belt
- A Poly-v-belt which wraps around several pulleys and idlers
- Service
-
- Periodic maintenance usually carried out by a garage; includes changing the oil and oil filter, checking the brakes, tires, ignition (usually changing the spark plugs), electrical, fuel and cooling systems, and taking the vehicle on a test run to check the steering, suspension, and transmission systems as well as the performance of the engine and brakes.
- To carry out a service on a vehicle.
- Serviceable hermetic
- Hermetic unit housing containing motor and compressor assembly by use of bolts or cap screws.
- Service brake
-
- A foot-operated brake used for retarding, stopping, and controlling the vehicle during normal driving conditions
- The primary brake system controlled by the brake pedal, operates the friction assemblies at all four wheels, and slows or stops the car in normal driving.
- Service brake valve
- A foot-operated unit which is used for graduated control of all the brakes in the service brake system.
- Service Consultant
- At many dealerships, the person responsible for receiving cars brought to the service department, in order to estimate the nature and cost of repairs and when the work will be completed. Also called Service writer
- Service factor
- (SF)
- A measure of the overload capacity designed into an electric motor. A 1.15 SF means the motor can deliver 15 percent more than the rated hp without injurious overheating.
- A multiplier that, when applied to the rated power, indicates a permissible power loading that may be carried under the conditions specified for service factor.
- Service hose
- Specially manufactured hose designed to withstand the operating pressures of air conditioner system and equipped with threaded fittings that can be attached to service valves, manifold gauge sets, vacuum pumps, refrigerant containers, etc.
- Service interval
- The time or mileage between services (e.g., 12 months or 10,000 miles, whichever should come first)
- Service manifold
- Chamber equipped with gauges and manual valves, used by service technicians to service refrigerating systems.
- Service manual
- A handbook published by a vehicle manufacturer or a specialized publishing company that contains instructions and Specifications for the maintenance and repair of a specific car. It may include Wiring diagrams and Troubleshooting guides. Most service manuals deal with only one make, model, or year, and nearly all are intended for professionals or the very experienced amateur.
- Service port
- A fitting, on stem-type service valves and some control devices, to which manifold gauge set service hoses can be connected
- Service valve
-
- The high or low side service valves.
- Manually operated valve mounted on refrigerating systems used for service operation.
- Device used to check pressures, service, and charge refrigerating systems.
- Service writer
- At many dealerships, the person responsible for writing repair orders (work orders) is the service writer. He communicates to the mechanic and service manager the problems in your vehicle that you have outlined. He also Estimates the nature and cost of repairs and gives you an idea when the work will be finished. Also called Service consultant
- Servicing
- To carry out a Service
- Servo
-
- A servo motor supplies power to a servo-mechanism. A servo-mechanism is a low-power device (electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic) used to put in operation and control a more complex or powerful mechanism.
- An oil operated device used to push or pull another part, such as tightening the transmission brake bands.
- Any system used to assist a mechanism to operate with greater force than that initially applied to it.
- Abbreviation for Servomechanism
- Servo action brakes
- Brakes so constructed as to have one end of the primary shoe bearing against the end of the secondary shoe. When the brakes are applied, the primary shoe attempts to move in the direction of the rotating drum and in so doing applies force to the secondary shoe. This action, called servo action, makes less brake pedal pressure necessary and is widely used in brake construction.
- Servo brake
-
- A drum brake in which the shoes are arranged so that one shoe helps to apply the other, to create a self-energizing effect in both shoes
- A drum brake in which brake shoes are linked, such that the braking force of one shoe amplifies the input of the other shoe(s).
- Servomechanism
- A device that provides power assistance to operate a control (e.g., a brake or clutch)
- Servo motor
-
- A small electric motor that supplies power to a Servomechanism
- A calibrated vacuum or electrical motor used to position valves or doors in an automotive air conditioning system.
- Servos
- Servos apply certain mechanical functions. For instance, if first gear is actuated by the application of a band, the servo is what applies that band. The servo is nothing more than a piston that is connected to a mechanical linkage, moved by hydraulic pressure. When the need for a certain application arises, oil pressure moves the servo and the servo makes the application.
- Setback Axle
- The front steering axle moved rearward from the generally accepted standard position. Advantages Shorter turning radius and more of a vehicle's weight shifted to the front axle.
- Set screw
-
- A fully threaded bolt with a parallel shaft. It is used to secure metal parts together (such as a hub or wheel to a shaft); can have a variety of heads, the most common being hexagonal, round or countersunk
- An externally threaded fastener with or without a head and having a formed point, designed to prevent relative movement of parts when screwed through one part upon or into another part.
- Set Screw Points
- A screw with various type points, cup, cone, flat, oval, half dog, full dog, hanger or knurled, used to hold or 'set' a collar on a shaft or hold pieces of this kind against movement. Screws are usually short, threaded entire length with the various type points for different applications against this movement.
- Setting time
- The time required for a adhesive, sealer or coating to approach maximum strength and firmness as it dries or sets
- Settle
- To sink to the bottom (of a liquid). The weight of the pigments in a paint varies greatly depending on their color. Heavy pigments give color, opacity, and specific properties to the paint. Some pigments weigh seven or eight times as much as the liquid part of the paint and because of this, they tend to settle to the bottom of the container
- Settling
- The Pigment in the paint collecting at the bottom of the spray gun container.
- Set-up
-
- Premature vulcanization of a rubber compound during processing or storage.
- The action of a gel-like substance which goes from a liquid to a rubbery solid or when a paste turns solid.
- Seventy-five (Cadillac)
- A 1936-76 Cadillac vehicle brand of which the Sedan/Limo for 1946-70 are milestone cars. Also see history of Cadillac.
- Seville
- A model of automobile manufactured by the Cadillac division of General Motors from 1975 to 2004. The name was also used on some Eldorados as Eldorado Seville from 1956 to 1960.
- Sew-up tire
- A bicycle tire with an Inner tube stitched inside the casing; also known as a tubular.